본 글은 주재걸교수님의 인공지능을 위한 선형대수 강의를 듣고 정리한 내용입니다.
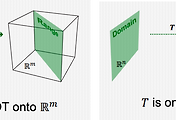
- A transformation, function, or mapping, 𝑇 maps an input 𝑥 to an output 𝑦
- Mathematical notation: 𝑇: 𝑥 ↦ 𝑦
- Domain(정의역) : Set of all the possible values of x
- Co-domain(공역) : Set of all the possible values of y
- Image(함수의 상) : a mapped output 𝑦, given x
- Range(치역) : Set of all the output values mapped by each 𝑥 in the domain
- 하나의 정의역에 하나의 화살표만 정의

Linear Transformation
A transformation (or mapping) 𝑇 is linear if:
- I. 𝑇(𝑐𝐮 + 𝑑𝐯) = 𝑐𝑇(𝐮) + 𝑑𝑇(𝐯) for all 𝐮, 𝐯 in the domain of 𝑇 and for all scalars 𝑐 and 𝑑
- Simple example: 𝑇: 𝑥 ↦ 𝑦, 𝑇(𝑥) = 𝑦 = 3𝑥
- y = 3x + 2 와 같은 경우는 선형 변환이 성립하지 않음
- 내적을 이용하면 선형 변환 가능

- 𝑇 ∶ ℝ𝑛 → ℝ𝑚 이 선형 변환인 경우, T는 matrix와 vector의 곱으로 나타낼 수 있다. (𝑇 x = 𝐴x for all x ∈ ℝ^n)
- In fact, the 𝑗-th column of 𝐴 ∈ ℝ𝑚×𝑛 is equal to the vector 𝑇 e𝑗 , where e𝑗 is the 𝑗-th column of the identity matrix in ℝ𝑛×𝑛
- e1 = [1,0,0,...,0]T, e2 = [0,1,0,...,0]T
- the matrix 𝐴 is called the standard matrix of the linear transformation T
'Study > 선형대수학' 카테고리의 다른 글
| 3-1. Least Squares Problem (0) | 2022.01.01 |
|---|---|
| 2-6. 전사함수와 일대일함수 (0) | 2021.12.30 |
| 2-4. 부분공간의 기저와 차원 (0) | 2021.12.29 |
| 2-3. 선형독립과 선형종속 (0) | 2021.12.28 |
| 2-2. 선형결합 (0) | 2021.12.28 |
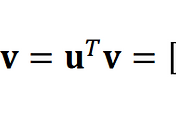


댓글