본 글은 주재걸교수님의 인공지능을 위한 선형대수 강의를 듣고 정리한 내용입니다.
Over-determined Linear Systems (#equations ≫ #variables)
- 보통의 경우 solution이 없음
- 근사적인 해를 구해 보는 것이 Least Squares Problem의 기본 개념
- 가장 근사치의 해를 어떻게 정의할 것인가?
1. Inner Product(내적)

Let 𝐮, 𝐯, and 𝐰 be vectors in ℝ𝑛 , and let 𝑐 be a scalar.
a) 𝐮 ∙ 𝐯 = 𝐯 ∙ 𝐮 (교환 법칙)
b) (𝐮 + 𝐯) ∙ 𝐰 = 𝐮 ∙ 𝐰 + 𝐯 ∙ 𝐰 (분배 법칙)
c) (𝑐𝐮) ∙ 𝐯 = 𝑐(𝐮 ∙ 𝐯) = 𝐮 ∙ (𝑐𝐯) (상수의 곱)
d) 𝐮 ∙ 𝐮 ≥ 𝟎, and 𝐮 ∙ 𝐮 = 𝟎 if and only if 𝐮 = 𝟎
∴ (𝑐1𝐮1 + ⋯ + 𝑐𝑝𝐮𝑝) ∙ 𝐰 = 𝑐1(𝐮1 ∙ 𝐰) + ⋯ + 𝑐𝑝(𝐮𝑝 ∙ 𝐰)
2. Vector Norm
The length (or norm) of 𝐯 is the non-negative scalar 𝐯 defined as the square root of 𝐯 ∙ 𝐯

For any scalar 𝑐, the length 𝑐𝐯 is 𝑐 times the length of 𝐯
3. Unit Vector
A vector whose length is 1 is called a unit vector
Normalizing a vector: Given a nonzero vector 𝐯, if we divide it by its length, we obtain a unit vector 𝐮 = 1/||𝐯|| * 𝐯.
4. Distance between Vectors
For 𝐮 and 𝐯 in ℝ𝑛 , the distance between 𝐮 and 𝐯, written as dist (𝐮, 𝐯), is the length of the vector 𝐮 − 𝐯



5. Inner Product and Angle Between Vectors
Inner product between 𝐮 and 𝐯 can be rewritten using their norms and angle

6. Orthogonal Vectors
𝐮 ∈ ℝ𝑛 and 𝐯 ∈ ℝ𝑛 are orthogonal (to each other) if 𝐮 ∙ 𝐯=0

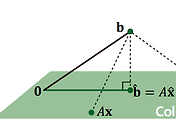
∴ Least Squares Problem
Now, the sum of squared errors can be represented as ||𝐛−𝐴𝐱||
: Given an overdetermined system 𝐴𝐱≃𝐛where 𝐴∈ℝ𝑚×𝑛, 𝐛∈ℝ𝑛, and 𝑚≫𝑛, a least squares solution 𝐱 is defined

'Study > 선형대수학' 카테고리의 다른 글
| 3-3. 정규방정식 (0) | 2022.01.03 |
|---|---|
| 3-2 Least Squares와 그 기하학적 의미 (0) | 2022.01.03 |
| 2-6. 전사함수와 일대일함수 (0) | 2021.12.30 |
| 2.5 선형변환 (0) | 2021.12.29 |
| 2-4. 부분공간의 기저와 차원 (0) | 2021.12.29 |
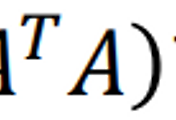

댓글