본 글은 Havard University Statistics 110 강의를 듣고 정리한 내용입니다.
Independent
Defn : Event A, B are independent if P(A∩B) = P(A)P(B)
completely different from disjointness(배반)
독립 : A가 일어나는 일을 B는 알 수 없다
배반 : A가 일어나면 B는 일어날 수 없다.
A, B, C are independent if P(A,B) = P(A)P(B), P(A,C) = P(A)P(C), P(B,C) = P(B)P(C), P(A,B,C) = P(A)P(B)P(C)
비슷하게 A1 , ... , An의 사건이 있을때, 몇개의 사건을 뽑아도 모두 독립이다.
Newton-Pepys Problem
공평한 주사위를 가지고 있을 때, 어떤 사건이 가장 확률이 높은가?
A : 6개의 주사위중 적어도 하나의 6이 나올 확률 <- truth
B : 12개의 주사위중 적어도 2개의 6이 나올 확률
C : 18개의 주사위중 적어도 3개의 6이 나올 확률 <- pepys
P(A) = 1 - (5/6)^6 ≒ 0.665
P(B) = 1 - (5/6)^12 - 12 C 1 (1/6)(5/6)^11 ≒ 0.619
P(C) = 1 - (5/6)^18 - 18 C 1 (1/6)(5/6_^17 - 18 C 2 (1/6)^2(5/6)^16 ≒ 0.597
equation 1 - ∑(k = 0 ~ n) 18 C k (1/6)^k (5/6)^18-k
Conditional probability(조건부 확률)
How should you update prob/beliefs/uncertainty based on new fvidence?
Defn P(A|B) -> B가 일어났을 때 A가 일어날 사건
P(A|B) = P(A∩B) / P(B) if P(B) > 0
Intuition 1 : pebble world

P(A|B) : get rid of pebbles in B^c = renormalize to make total mass 1 again
Intuition 2 : frequentist world(빈도주의 학자 세계)

Circle reps where B occur among those, what fraction of time A also occur?
정리
- P(A∩B) = P(B)P(A|B) = P(A)P(B|A)
- P(A_1, A_2, ... A_n) = P(A_1)P(A_2|A_1)P(A_3|A_1,A_2) ... P(A_n| A_1,..., A_{n-1})P(A1,A2,...An)=P(A1)P(A2∣A1)P(A3∣A1,A2)...P(An∣A1,...,An−1)
- P(A |B) = {P(B|A)P(A)} / {P(B)} → 이를 베이즈의 정리(Bayes’ Theorem)라 한다.
'Study > 통계학' 카테고리의 다른 글
| 6. Monty Hall 문제와 심슨의 역설 (Monty Hall, Simpson's Paradox) (0) | 2022.01.18 |
|---|---|
| 5. 조건부 확률과 전확률정리 (Conditioning Continued, Law of Total Probability) (0) | 2022.01.17 |
| 3. Birthday Problem과 확률의 특성 (Birthday Problem, Properties of Probability) (0) | 2022.01.13 |
| 2. 해석을 통한 문제풀이 및 확률의 공리 (Story Proofs, Axioms of Probability) (0) | 2022.01.11 |
| 1. 확률과 셈 원리 (Probability and Counting) (0) | 2022.01.10 |
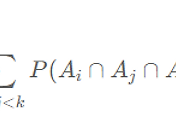
댓글