본 글은 Havard University Statistics 110 강의를 듣고 정리한 내용입니다.
Thinking conditionally is a condition for thinking
How to solve a problem?
- 간단한 케이스와 극단적인 케이스 적용
- 문제를 더 작은 조각으로 나누어서 해결

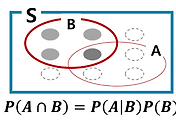
Let A1, A2, ... An partition of S -> disjoint, ∑An = S
Then P(B) = P(B∩A1) + P(B∩A2) + ... + P(B∩An) = P(B|A1)P(A1) + ... + P(B|An)P(An) -> law of total probability(전체 확률의 정리)
Ex. 52장 중 2개의 랜덤한 카드를 뽑았을 때의 조건부 확률
Find P(both aces | have ace), P(both aces | have Ace of spade)
- P(both aces | have ace) = P(both aces) / P(have ace) = {4 C 2 / 52 C 2} / {1 - 48 C 2 / 52 C 2 } = 1 / 33
- P(both aces, have ace) == P(both aces)
- P(both aces | have Ace of spade) = 3 / 51 = 1 / 17
Ex. 환자가 특정 질병에 대한 검사에서 양성을 받았을 때의 조건부 확률(질병에 걸린 사람은 전체의 1%)
* test는 95%의 정확도를 가진다.
* event D : 환자가 질병을 가지는 사건
* event T : 환자가 양성판정을 받는 사건
P(T|D) = 0.95 = P(T^c | D^c) -> 환자가 질병을 가지는 경우 95%의 확률로 양성 판정을 내린다.
Find P(D|T) = P(T|D)P(D) / P(T) = P(T|D)P(D) / {P(T|D)P(D) + P(T|D^c)P(D^c)} = 0.16
Biohazards
- confusing P(A|B), P(B|A) (prosecuto's fallacy 검사의 오류)
- confusing P(A) 'prior' with P(A|B) 'posterior' (사전확률과 사후확률에 대한 혼동)
- confusing independence with conditional independence (독립과 조건부 독립의 혼동)
Defn Events A, B are conditionally independence, given C
if P(A∩B | C) = P(A|C) P(B|C)
- Does conditional independence given C imply independence => No
- chess opponent of unknown strength, 이전의 경기들이 후의 경기 결과를 예측하는데 도움을 주기 때문에 independence 하지 않다. (경기들은 조건부 독립, 경기결과는 조건부독립(상대의 실력이 주어졌을 때)이지만 독립은 아니다.)
- Dose independence given C imply conditional independence? => No
- Counter Ex. event A : firealarm goes off
- caused by : F : fire, C : popcorn, suppose F, C indep.
- P(F|A,C^c) = 1 is independent, C를 제거하면 F는 일어날 수 밖에 없기 때문에 독립이지만 화재 경보가 울렸다는 조건 하에는 독립이 아니다. 화재 경보가 울리고 이를 설명하려면 둘은 종속이게 된다.
'Study > 통계학' 카테고리의 다른 글
| 7. 도박꾼의 파산 문제와 확률변수 (Gambler's Ruin and Random Variables) (0) | 2022.01.20 |
|---|---|
| 6. Monty Hall 문제와 심슨의 역설 (Monty Hall, Simpson's Paradox) (0) | 2022.01.18 |
| 4. 조건부 확률 (Conditional Probability) (0) | 2022.01.13 |
| 3. Birthday Problem과 확률의 특성 (Birthday Problem, Properties of Probability) (0) | 2022.01.13 |
| 2. 해석을 통한 문제풀이 및 확률의 공리 (Story Proofs, Axioms of Probability) (0) | 2022.01.11 |
댓글