본 글은 주재걸교수님의 인공지능을 위한 선형대수 강의를 듣고 정리한 내용입니다.
Gram-Schmidt
Orthogonal 하지 않은 두 벡터에 대해 아래 식을 통해 orthogonal한 벡터를 만들어 준다.

v2 vector를 v1(=u1) 방향에 대하여 projection 해준다. => v2 vector

{𝐱1, 𝐱2, 𝐱3} is clearly linearly independent and thus is a basis for a subspace 𝑊 of ℝ4 . Construct an orthogonal basis for W
Solution
- Let 𝐯1 = 𝐱1 and 𝑊1 = Span {𝐱1} = Span{ 𝐯1}
- Let 𝐯2 be the vector produced by subtracting from 𝐱2 its projection onto the subspace 𝑊1

𝐯2 is the component of 𝐱2 orthogonal to 𝐱1, and {𝐯1, 𝐯2} is an orthogonal basis for the subspace 𝑊2 spanned by 𝐱1 and 𝐱2.
- Let 𝐯3 be the vector produced by subtracting from 𝐱3 its projection onto the subspace 𝑊2. Use the orthogonal basis {𝐯1, 𝐯2′} to compute this projection onto 𝑊2

QR Factorization
If 𝐴 is an 𝑚 × 𝑛 matrix with linearly independent columns, then 𝐴 can be factored as 𝐴 = 𝑄𝑅, where 𝑄 is an 𝑚 × 𝑛 matrix whose columns form an orthonormal basis for Col 𝐴 and 𝑅 is an 𝑛 × 𝑛 upper triangular invertible matrix with positive entries on its diagonal

'Study > 선형대수학' 카테고리의 다른 글
| 4-2. 영공간과 직교여공간 (0) | 2022.01.05 |
|---|---|
| 4-1. 고유벡터와 고유값 (0) | 2022.01.05 |
| 3-4. Orthogonal Projection (0) | 2022.01.04 |
| 3-3. 정규방정식 (0) | 2022.01.03 |
| 3-2 Least Squares와 그 기하학적 의미 (0) | 2022.01.03 |


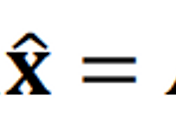
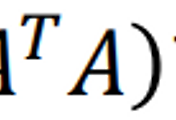
댓글